How Does Temperature Affect the Conductivity of a Conductor?
Let’s Consider the effect of increasing the temperature on the conductivity of conductors.
Let's look at the factors that go into conductivity and consider how each of these are affected:
sigma = n q m
- First
consider what will happen to n as temperature increases. The electrons
that are charge carriers in a conductor will gain energy and go
into higher energy levels. However, these energy levels are all
still in the valance band. So the number of charge carriers will not change for a conductor with an increase in temperature.
- Now consider q. As temperature increases, the charge on each carrier will not change.
- Finally,
what happens to the mobility? Recall that mobility is the drift
velocity divided by the electric field strength. Temperature won't
affect the electric field strength. But it will decrease the drift
velocity because as the temperature
increases, the atomic vibrations will increase, which will cause more
collisions of the electrons with the crystal lattice. Hence the drift
velocity will decrease.
Conclusion:
The electrical conductivity of a conductor will decrease with an increase in temperature!
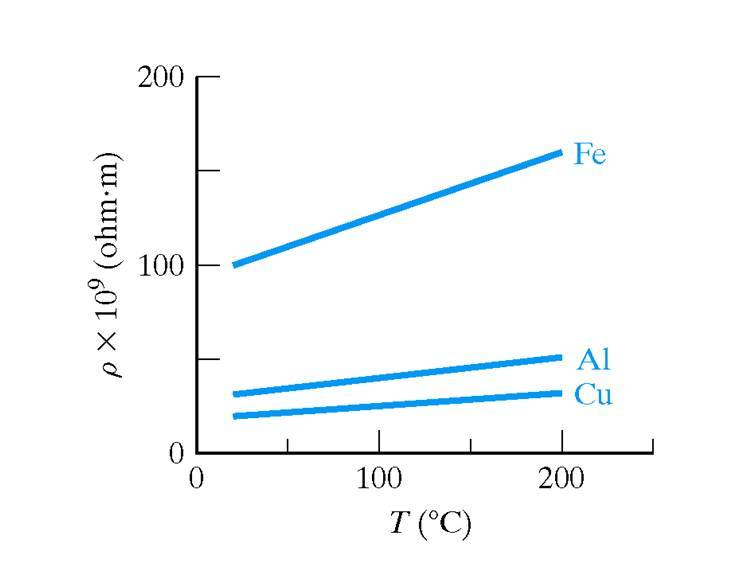
The
relationship is not linear, however, if we consider the resistivity,
which is the reciprocal of conductivity, we do get a linear
relationship:
rho = rhoroomTemp [1 + alpha(T - Troom)]
where rhoroomTemp is the room temperature resisitvity and alpha is the temperature coefficient of resistivity.