Wood
Wood - a naturally occuring fiber-reinforced composite material
Wood is an example of a naturally occurring fiber-reinforced composite material. Is an important structural material (used for houses, buildings, bridges, etc.) that, by tonnage, is used more than steel or concrete in the U.S. It is also used to make composite materials such as plywood, particleboard, and paper.
There are hardwoods such as maple and oak and softwoods such as
cedar and pine. Both types consist mainly of a complex array of
cellulose cells reinforced by a
polymeric substance called lignin and other organic compounds.
Structure of Wood
Here is a schematic of the microstructure of a soft wood.
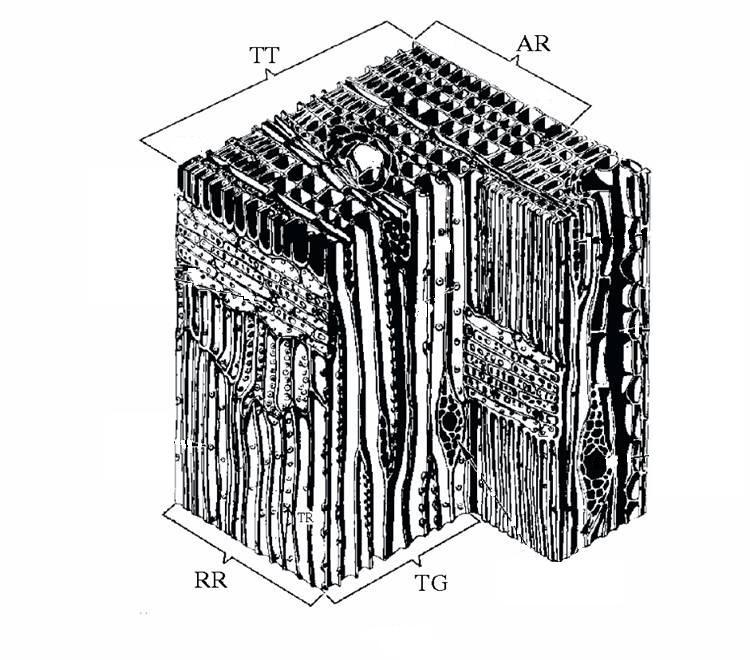
The structural features are:
- TT is a cross-sectional face
- RR is a radial face
- TG is a tangential face
- AR is an annual ring
Wood is Anisotropic
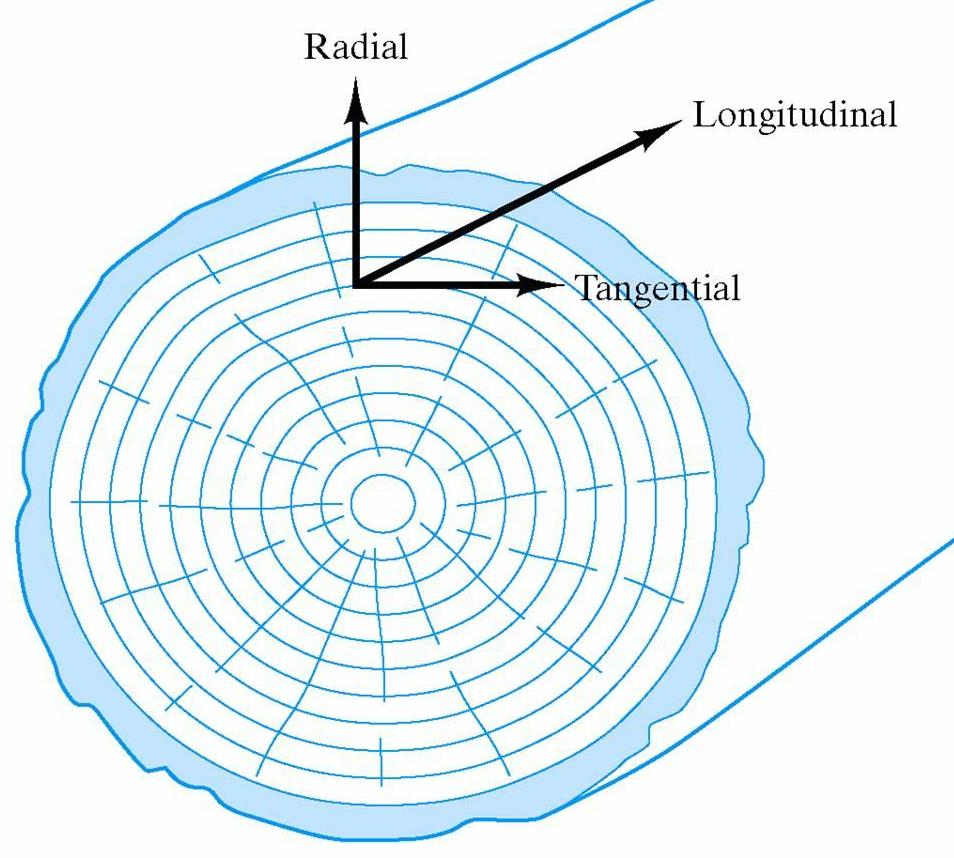
Wood is highly anisotropic. The properties will be different in the radial, longitudinal and tangential directions.
For example:
- Wood's tensile strength is much greater in the direction parallel to the tree stem (longitudinal direction).
- Wood's compressive strenght parallel to the grain (tangential direction) is higher than that perpendicular to
the grain (radial direction) by a factor of about 10 because covalent bonds act in the
longitudinal direction whereas hydrogen bonds act in the direction
perpendicular to the grain.
Wood and Moisture
The moisture content will affect the properties of wood.
wood moisture content (wt %) = (weight of water in sample / weight of dry wood sample) x 100 %
The green
condition of wood is the moisture content in it while it is living. Greenwood shrinks as moisture is eliminated and causes distortion depending on which kind of cut the wood comes from. Kiln-dried wood is denser and
stronger than wood in the green condition because without the water
hydrogen bonding is stronger.

