
GE 345: Week 2
Circulatory System -- Electrical Activity
Updated by Tracey 8 June 02
Intro | The Heart | Electrical Activity | Hemodynamics | Circulation |
The heart contracts in response to electrical stimulus which spreads throughout the muscle from nodes. The action potential causes release of Calcium ions into the sarcoplasm as it spreads. The calcium then spreads to the myofibrils where they catalyze the contraction process.
EKG
Sum of electrical activity in the heart, which can be picked up extracellularly by applying electrodes to the skin. When muscle tissue depolarizes, the normally negative potential inside the fiber is lost and the membrane potential reverses, so it becomes slightly positive inside. When the tissues repolarize, the normal potentials are restored.
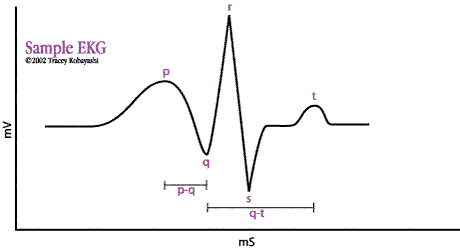
- P Wave: atrial depolarization
- QRS Complex: atrial repolarization & ventricular depolarization
- T wave: ventricular repolarization
- P-Q Interval: time between beginning of atrial and ventricular contractions, usually about .16 second
- Q-T Interval: Ventricular contraction, usually about .30 second
When Things Go Wrong
Disturbances in the heart's electrical patterns cause it to beat out-of-sync, which disrupts the normal EKG pattern. These disturbances are commonly called arrhythmias. Two common arrhythmias:
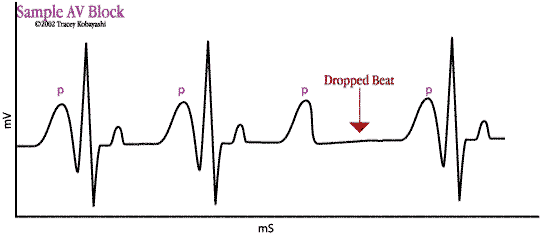
- Atrioventricular Block
Conduction rate through the A-V bundle (aka: Bundle of His) is altered. With an incomplete block, conduction impulse rate is slowed, and there will be "dropped beats" of the ventricles. With a complete block, there will be no relation between the rhythm of the atria and ventricles, since the ventricles beat at their own natural rate rather than being controlled by the atria. Causes include:- Ischemia of A-V junctional fibers
- A-V bundle compressed by scar tissue or calcified portions of the heart
- Inflammation of the A-V bundle or its fibers
- Overstimulation of the heart by the vagi
- Premature Contraction (aka: extrasystole)
Heart contracts sooner than normal. Mostly from ectopic foci, which admit abnormal impulses at odd times. Ectopic foci can be caused by local areas of ischemia, small calcified plaques in the heart which press against adjacent cardiac muscle irritating some of the fibers, or toxic irritation from drugs, nicotine, caffeine, etc.
Intro | The Heart | Electrical Activity | Hemodynamics | Circulation |