
GE 345: Week 5
Stomach
| Intro | Mouth | Stomach | Sm Int | Colon | |
Motor functions of the the stomach include:
- Store large quantities of food until it can be processed in the duodenum
- Mix food with gastric secretions to form chyme, a semifluid mixture. Slow peristaltic waves both mix and transport food. Hunger contractions can occur when the stomach has been empty for several hours.
- Empty food slowly into the small intestine at a rate suitable for digestion and absorption in the small int.
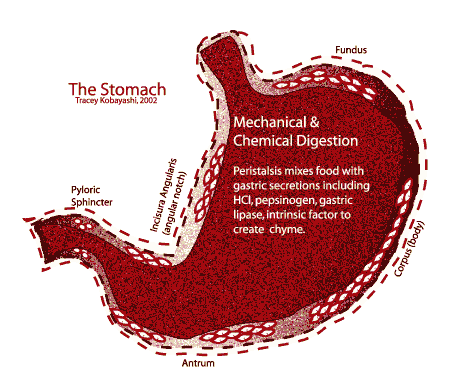
Antral peristaltic contractions move chyme toward the pylorus, the distal opening of the stomach. The chyme leaves the stomach through the pyloric sphincter into the duodenum. Stomach emptying is influenced somewhat by food volume, and hormones such as gastrin. It is influenced to a greater extent by feedback from the duodenum, based on the amount of chyme in the small intestine, and the contents of the chyme in the small intestine.
Secretion & Digestion
Mucus-secreting cells secrete...mucus! Mucus mixes with the food to form chyme.
Oxyntic/Gastric glands in body of the stomach secrete mucus and:
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): provides acid medium needed for pepsin and further hydrolizes starches.
- Pepsinogen: forms pepsin when it contacts HCl. A proteolytic enzyme in an acidic environment, pepsin splits proteins into proteoses, peptones and large polypeptides. Pepsin is important for digesting collagen, a major constituent in fibrous tissues of meat.
- Intrinsic Factor: essential for B12 absorption in the ileum.
- Gastric Lipase: digests a minute amount of fat.
Pyloric glands in the antrum secrete mucus, some pepsinogen and gastrin.
Most secretory nerves secrete ACH, which stimulates secretory activity of both HCl and pepsinogen.
The stomach does not typically absorb fluid or nutrients. A few lipid-soluble substances such as alcohol and some drugs can be absorbed in small quantities.