
GE 345: Week 1
II. Cells (Histology)
Updated by Tracey 8 June 02
Overview | Gross Cell | Cell Structure | Cell Innards | Synthesis
The Basis of Life
Homeostasis: constant conditions in the internal environment. Maintained by organ & tissue processes, which rely on 75 trillion cells functioning in an aqueous environment.
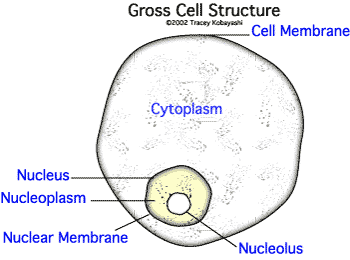
Each cell performs specialized functions, but all cells have a few things in common:
- Use oxygen with carbohydrate, fat or protein to produce energy required to function.
- Mechanisms of converting nutrients into energy are similar.
- Deliver end-products of reactions into surrounding fluids.
- Reproduction (some can't) by division.
Water, Bringer of Life
Cells function in a fluid environment.
- Extracellular Fluid(aka Internal Environment): Fluid surrounding the cells. Provides consistent environment for functions. Transports sodium, chloride & bicarbonate ions, and nutrients to the cells. Carries carbon dioxide and other by-products from cells to lungs for exhalation and kidneys for excretion.
- Intracellular Fluid: Fluid inside cells. Contains potassium, magnesium and phosphate ions. Provides environment for cell processes to function.
Overview | Gross Cell | Cell Structure | Cell Innards | Synthesis