
GE 345: Week 1
III. Basic Cell Structure and Function
Overview | Gross Cell | Cell Structure | Cell Innards | Synthesis
Each cell is a living structure which can survive indefinitely, and in some cases reproduce, provided the surrounding fluids contain appropriate nutrients.
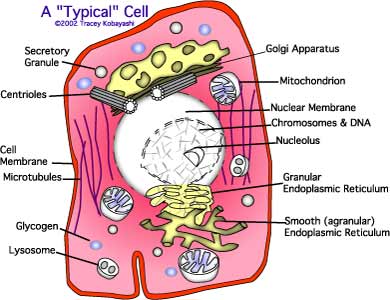
A Basic Cell...
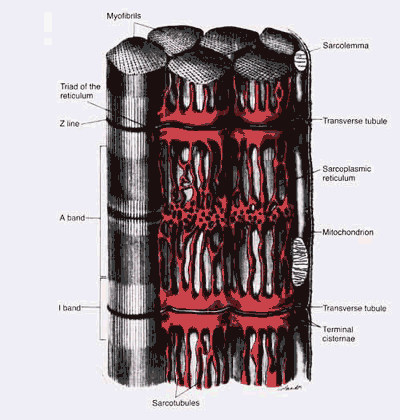
A Muscle Cell...
Protoplasm: collective term for everything making up the cell. Composed mainly of: water; electrolytes; proteins; lipids; and carbohydrates.
Membranous Structures
Lipid membranes line the cell and its structures.
- Prevent free movement of water and water soluble substances between compartments.
- Embedded proteins interrupt barrier's continuity, providing pathways for passage of specific substances.
- Many of these proteins also act as enzymes, which assist chemical reactions
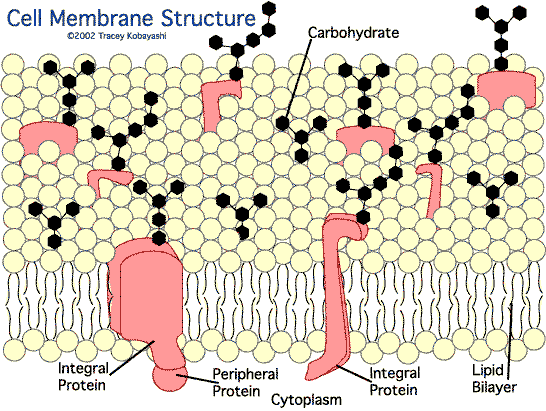
Cell Membrane
Lipid bilayer structure -- lipid film 2 molecules thick, composed of phospholipids and cholesterol. Creates impermeable barrier to water-soluble substances (ions, glucose, urea), while allowing fat-soluble (oxygen, alcohols) substances to penetrate. Each molecule has two parts:
- Hydrophilic (water soluble) portion: phosphate radical of the phospholipid; hydroxyl radical of cholesterol.
- Hydrophobic (fat soluble) portion: fatty acid radicals of phospholipid; steroid nucleus of cholesterol.
Natural tendency to form 2 molecule-thick membrane:
- Fatty portions attract each-other to form the center.
- Hydrophilic portions project to the surrounding water.
Membrane is fluid -- portions flow from one point to another. Proteins diffues to all areas of the membrane.
Cell membrane proteins are mostly glycoproteins. There are 2 types:
- Integral Proteins protrude all the way through the membrane. Provide structural channels for ions to diffuse between ecf and icf. Some act as carriers to transport substances too large to diffuse.
- Peripheral Proteins attach to surface only. Almost entirely inside membrane, normally attached to an integral protein. Act as enzymes.
Membrane carbohydrates most commonly occur combined with proteins and lipids as glycoproteins and glycolipids. Mostly protrude to outside of the cell. Proteoglycans, carbohydrate bound together by small protein cores, attach loosely to outside. Cell surface often has a carbohydrate coat, the glycocalyx. Functions:
- Many have neg. charge, so cell surface is also negatively charged.
- Glycocalyx of some cells attach to glycocalyx of other cells.
- Receptors for binding hormones like insulin, stimulating specific cell activities.
- Interact with immune reactions
Overview | Gross Cell | Cell Structure | Cell Innards | Synthesis