
GE 345: Week 4
Skeletal Muscle
| Potential | Skeletal Muscle | Myofibrils, NM Interaction | Contraction | Fun Facts | |
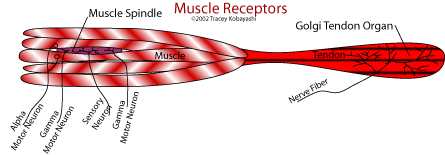
Skeletal muscles are composed of bundles of fibers called fasiculi (sing. fasiculus). Each muscle fiber (cell) is innervated by a nerve located near its middle.
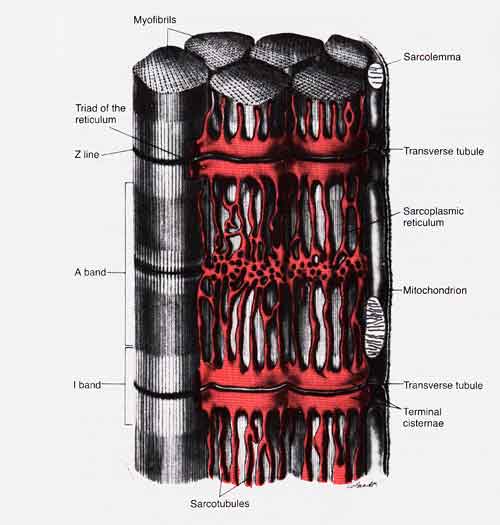
Muscle fiber constituents include:
- Myofibrils: hundreds to thousands of actin and myosin filaments interact in each fiber to control muscle contraction.
- Sarcolemma: muscle fiber cell membrane. Consists of a true cell membrane, called the plasma membrane, and an outer coat composed of a thin layer of polysaccharide with collagen fibrils. The sarcolemma fuses with a tendon fiber at the end of the muscle fiber. The tendon fibers in turn make up the tendons, which insert into the bones.
- Sarcoplasm: matrix in which the myofibrils are suspended. Contains usual cell constituents as well as high amounts of potassium, magnesium, phosphate, protein enzymes, and mitochondria, which lie between and parallel to the myofibrils to supply the large amounts of ATP needed for muscle contraction.
- Sarcoplasmic Reticulum: replaces the ER. Terminal cisternae of the SR abut the T-tubules.
- Transverse Tubules (T-Tubules): extensions of the cell membrane which penetrate the fiber, interlacing through all myofibrils. Assures AP reaches all parts of the fiber.
| Potential | Skeletal Muscle | Myofibrils, NM Interaction | Contraction | Fun Facts | |